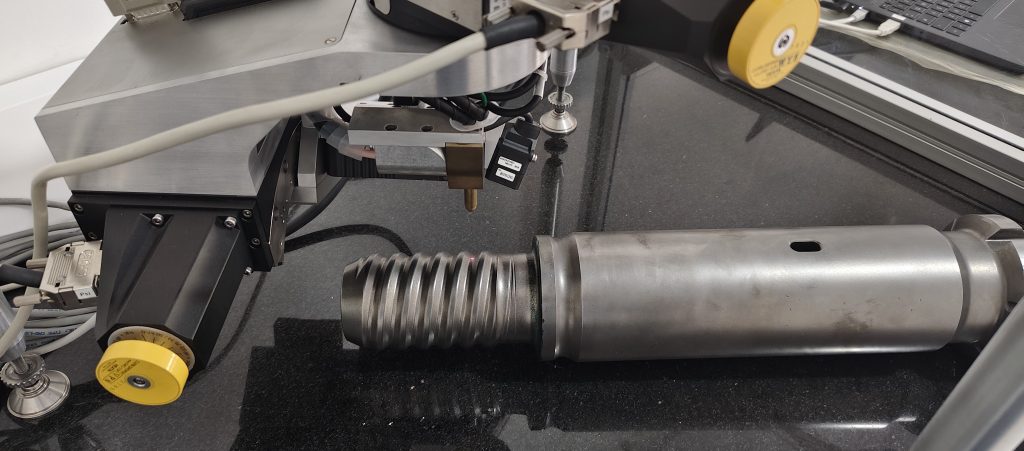
Why XRD residual stress analysis is critical for shot peening performance
Manufacturers in demanding industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy manufacturing frequently encounter challenges related to unexpected component failures and reduced product lifespan. Often, these issues stem from residual stresses introduced during manufacturing processes, notably shot peening. Precisely measuring and managing these internal stresses is key to optimizing component performance and ensuring consistent quality.
What is X-ray Diffraction (XRD)?
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) is a highly accurate, non-destructive testing method used to analyze residual stresses in metal surfaces. By leveraging this advanced technology, manufacturers can:
- Significantly improve fatigue life of components
- Prevent stress corrosion cracking
- Ensure high-quality and consistent manufacturing outcomes
How XRD optimizes shot peening
XRD technology precisely quantifies internal stresses by measuring how X-rays diffract through a component’s crystal lattice. This detailed stress profiling allows manufacturers to:
- Understand stress distribution clearly
- Optimize shot peening processes more effectively
- Enhance the reliability and durability of finished components
Introducing Winoa-2Effe Peening Center’s specialized XRD services
At our state-of-the-art Winoa-2Effe Peening Center in Pune, India, we offer specialized XRD residual stress analysis services. Our team of experts collaborates closely with manufacturers to enhance surface treatments, improve component longevity, and optimize overall manufacturing processes.
Explore our services:

Contact us
Connect with our technical experts today to enhance the durability and reliability of your components.
Technical overview: How XRD technology works
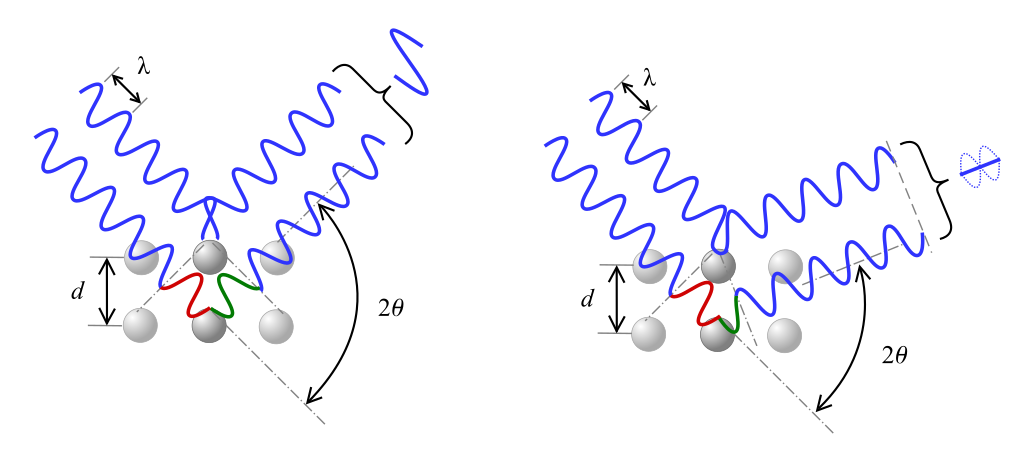
X-ray Diffraction (XRD) accurately measures internal stresses using the principle of Bragg’s Law, defined by the equation:
nλ=2dsinθ
where:
- n = Diffraction order
- λ = Wavelength of the X-ray
- d = Atomic spacing
- θ = Diffraction angle
When internal stresses exist, the atomic spacing shifts, altering the diffraction pattern. XRD captures these shifts precisely, revealing stress distributions and potential weaknesses.
Fig.1: Diagram of Bragg’s Law angle of deviation 2 theta, interference can be constructive (left) or destructive (right)
Advantages of XRD:
- Non-destructive surface analysis
- High sensitivity to small variations in stress
- Applicable to metals, ceramics, and composites
Limitations to consider:
- Limited measurement depth (typically 10-30 µm)
- Accuracy influenced by surface roughness and material texture
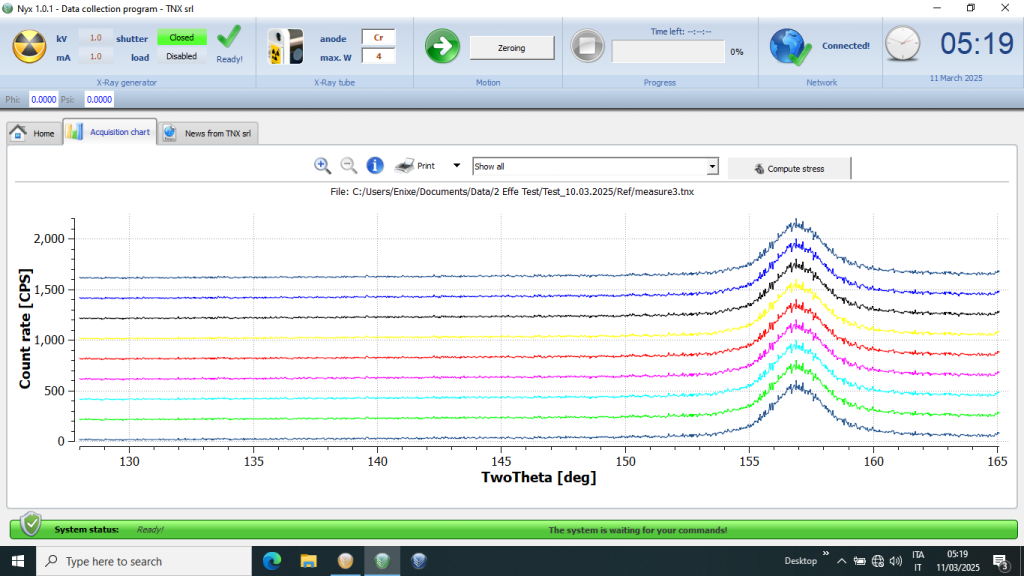
Fig. 2: X-ray diffraction pattern on steel component
Improving XRD measurement accuracy: Proper surface preparation, including meticulous abrasive blasting and polishing, significantly improves XRD accuracy and mitigates depth limitations.
Industry standards compliance: XRD measurements follow internationally recognized standards such as ASTM E915 and SAE J442, ensuring reliability and credibility of results.
Discover how Winoa can elevate your shot peening and surface treatment practices.
Contact our technical experts today to discuss your specific needs.
Explore our XRD capabilities
Enhance component durability and ensure top-quality control with our advanced X-ray Diffraction (XRD) services:
Residual Stress Analysis – Precise surface and sub-surface measurements for improved reliability.
Retained Austenite Analysis – Accurate assessment of austenite content to optimize mechanical performance.
Electro-Chemical Etching – Detailed sub-surface analysis with increments starting at 15 µm.
Standards Compliance – Certified to ASTM E2860-20, EN 15305:2008, and ISO 9001.
Equipment Model: ENIXE from TNX s.r.l. (Italy), manufactured in 2024.
Ready to enhance material integrity and manufacturing excellence?